How SMEs Can Automate Payments: 10 Proven Strategies to Boost Efficiency
In today’s
digital-first business landscape, automating payments is no longer a luxury but
a necessity for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). Manual processes
drain resources, increase errors, and limit agility. By embracing payment
automation, SMEs can streamline operations, save valuable time, and achieve
greater accuracy and compliance. This guide presents 10 proven strategies—plus
practical insights—to help SMEs transform their financial workflows for maximum
impact.
Table of Contents
1.
Why
Payment Automation Matters for SMEs
2.
Understanding
the Basics of Payment Automation
3.
Benefits
of Automating Payments for SMEs
4.
10
Proven Strategies for SMEs to Automate Payments
5.
Common
Challenges SMEs Face in Payment Automation
6.
Best
Practices for Successful Payment Automation
7.
Case
Studies: How SMEs Benefited from Payment Automation
8.
Conclusion:
The Future of Payment Automation for SMEs
9.
FAQs
About Payment Automation for SMEs
Why Payment Automation Matters for SMEs
Small and
medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) often juggle multiple financial
responsibilities while operating with limited resources. Manual payment
handling can be time-consuming, error-prone, and costly. That’s where payment
automation steps in—helping SMEs reduce inefficiencies, improve cash flow, and
build stronger financial control.
In today’s digital-first business environment, how SMEs can automate payments has become a critical question. By leveraging digital tools and automation technologies, SMEs can ensure accuracy, speed, and compliance in every financial transaction.
To explore practical options, check out our roundup of the top 10 payment solutions for SMEs in Delhi, Mumbai, and Bangalore.
Understanding the Basics of Payment Automation
Payment
automation refers to the use of digital technologies to streamline financial
transactions without constant human intervention. It covers processes like
accounts payable, payroll, vendor payments, and tax compliance. Instead of
spending hours on manual bookkeeping, SMEs can rely on software to handle
repetitive payment workflows with accuracy.
Key
components include:
1.
Invoice
digitization
2.
Automated
payment scheduling
3.
Integration
with banking APIs
4.
Real-time
reconciliation
This
foundation helps SMEs focus more on growth and less on repetitive admin tasks.
Benefits of Automating Payments for SMEs
Saving Time and Reducing Manual Work
Manual data
entry is prone to errors and eats up valuable staff hours. Automated systems
handle repetitive tasks—such as invoice approvals, recurring payments, and
payroll—within minutes, freeing employees for strategic work.
Improved Accuracy and Compliance
Automation
reduces the risk of errors like duplicate payments or missed deadlines. It also
ensures compliance with government regulations and tax requirements by
maintaining transparent digital records.
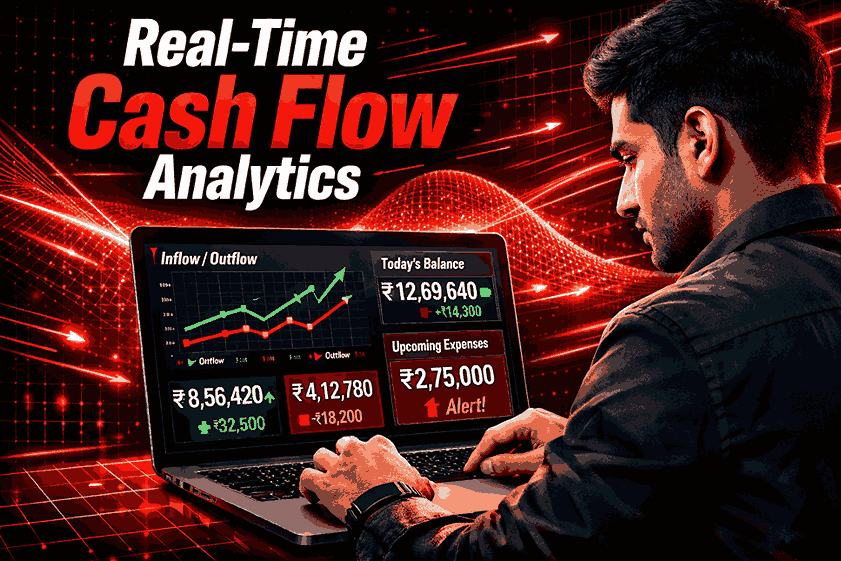
Better Cash Flow Management
Payment automation provides real-time visibility into cash flow. SMEs can track pending invoices, monitor receivables, and more effectively forecast their financial health. This level of control helps avoid cash shortages and strengthens relationships with vendors.
While automation streamlines processes, securing transactions is equally critical. Learn how SMEs can strengthen protection with our in-depth article on fraud prevention in digital payments.
10 Proven Strategies for SMEs to Automate Payments
1. Implementing Cloud-Based Accounting Software
Cloud
accounting platforms like QuickBooks, Zoho Books, and Xero allow SMEs to
automate payment reconciliation, generate reports, and track expenses in
real-time.
2. Using Automated Invoice Processing Tools
AI-driven
tools capture invoice data, verify accuracy, and trigger approvals. This cuts
down processing time from days to hours.
3. Setting Up Recurring Payments
For
recurring expenses like subscriptions, rent, or utilities, SMEs can automate
payments to avoid delays and penalties.
4. Integrating Payroll Automation
Payroll
platforms automate salary distribution, tax deductions, and employee
reimbursements—ensuring accuracy and timely payments.
5. Leveraging Bank APIs for Direct Transfers
By
connecting with banking APIs, SMEs can set up seamless, secure, and automated
fund transfers without manual interventions.
6. Adopting Digital Wallets and UPI for Quick Payments
In India,
UPI and digital wallets simplify B2B and B2C transactions, ensuring instant and
traceable payments.
7. Automating Vendor Payments with Smart Contracts
Blockchain-based
smart contracts enable automated, secure, and conditional vendor payments once
agreed-upon terms are met.
8. Using Expense Management Platforms
Platforms
like Expensify and SAP Concur help automate employee expense claims, approvals,
and reimbursements.
9. Automating Tax Payments and Compliance
SMEs can
integrate tax automation software to handle GST, VAT, or income tax filings
with accuracy.
10. Integrating Payment Automation with ERP Systems
ERP systems
like SAP or Oracle NetSuite centralize operations, enabling SMEs to connect
payments with supply chain, HR, and finance processes seamlessly.
Common Challenges SMEs Face in Payment Automation
1. Security and Fraud Concerns
Cybersecurity
risks remain a top concern. SMEs need strong encryption, authentication, and
fraud detection tools to safeguard payments.
2. Integration with Legacy Systems
Older
accounting systems may not integrate smoothly with new automation tools,
requiring upgrades or middleware solutions.
3. Training and Adoption Barriers
Employees
may resist new systems. Proper training and gradual adoption strategies can
help overcome this barrier.
Best Practices for Successful Payment Automation
1. Choosing the Right Tools and Vendors
SMEs should
evaluate scalability, features, and integration capabilities before selecting
automation software.
2. Ensuring Data Security and Compliance
Adopting PCI
DSS and GDPR-compliant systems ensures secure financial handling.
3. Regular Monitoring and Optimization
Regular
audits and performance checks ensure that automation remains aligned with
business goals.
Case Studies: How SMEs Benefited from Payment Automation
1. A Retail SME Streamlining Vendor Payments
A small
retail chain automated vendor payments using UPI-linked APIs. This reduced
processing time by 60% and improved vendor trust.
2. A Service-Based SME Automating Payroll
A
consultancy firm adopted payroll automation. Employee salaries were disbursed
in minutes, with tax compliance automatically handled—boosting employee
satisfaction.
Conclusion: The Future of Payment Automation for SMEs
The future of SMEs lies in digital-first finance operations. Automating payments not only improves efficiency but also creates room for scalability and innovation. SMEs that adopt automation today will have a competitive advantage tomorrow.
As digital adoption accelerates, tools like UPI AutoPay will play a key role in helping SMEs automate recurring transactions, reduce manual intervention, and scale with confidence.
FAQs About Payment Automation for SMEs
What is payment automation for SMEs?
Payment
automation is the use of software to handle financial transactions like
payroll, invoices, and vendor payments without manual intervention.
Is payment automation expensive for small businesses?
Not
necessarily. Many cloud solutions offer affordable monthly subscriptions
tailored for SMEs.
Can SMEs integrate payment automation with existing banking systems?
Yes, most
banks provide APIs and partnerships with accounting tools to support smooth
integration.
How secure are automated payment systems?
With proper
encryption, two-factor authentication, and compliance, automated payment
systems are highly secure.
Does payment automation eliminate the need for accountants?
No, it
doesn’t replace accountants but reduces their manual workload—allowing them to
focus on strategic financial planning.
Which industries benefit most from payment automation?
Retail,
services, manufacturing, and e-commerce SMEs benefit the most due to high
transaction volumes.